安卓版下载
安卓版下载
大小:14.63MB
下载:15949次
英语翻译官安卓版
- 支 持:Android
- 分 类:手机软件
- 大 小:14.63MB
- 版 本:
- 评 分:
- 开发者:
- 下载量:15949次
- 发 布:2024-11-28 06:33
手机扫码免费下载
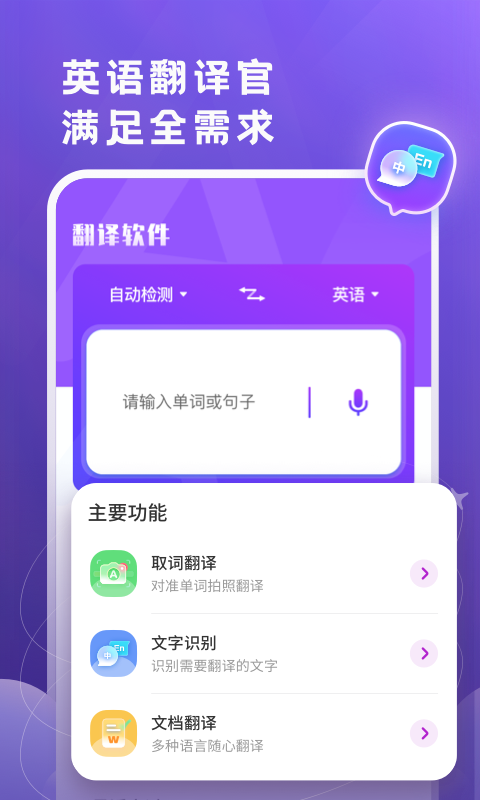
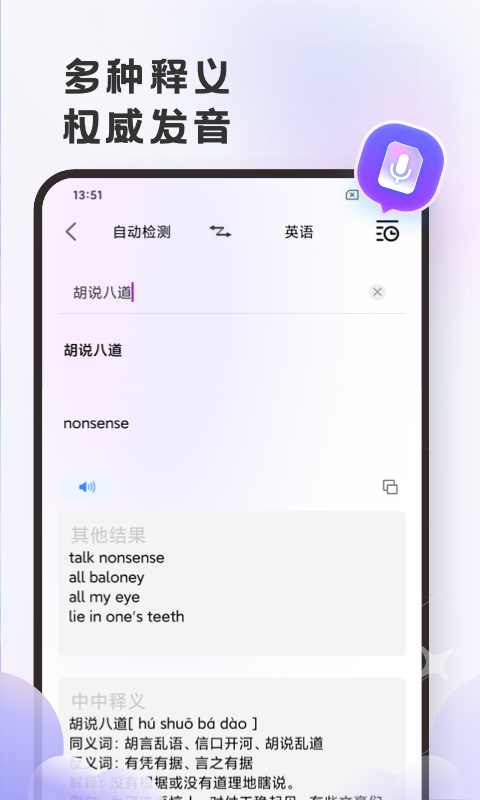
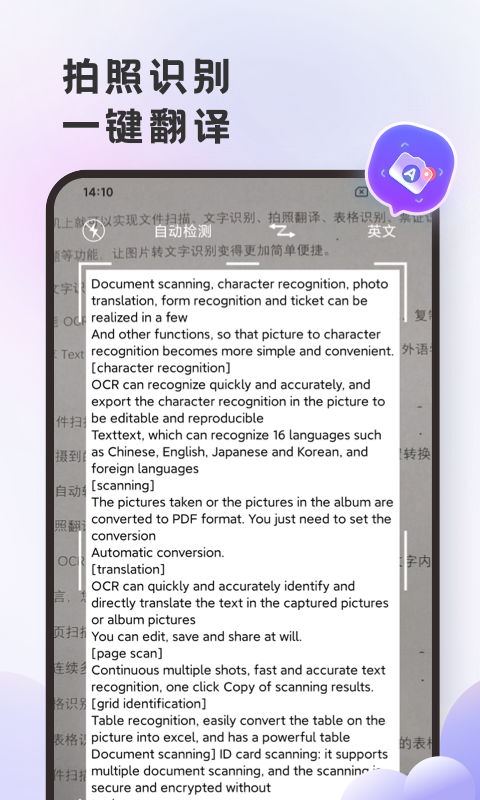
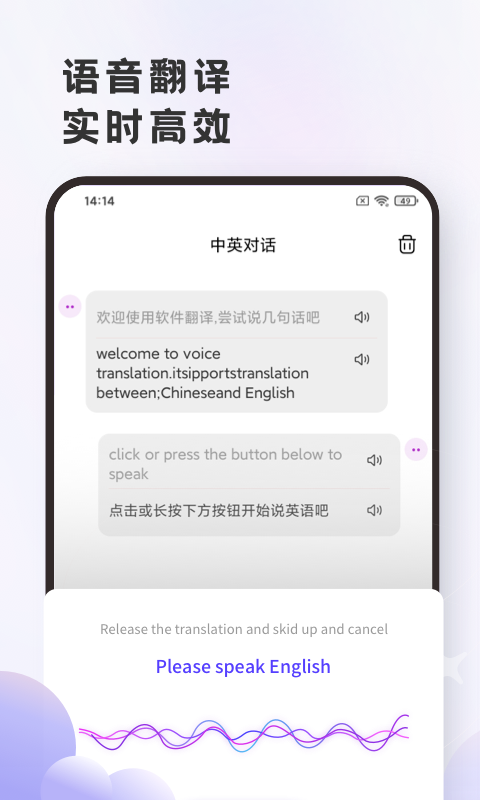
#英语翻译官安卓版截图
#英语翻译官安卓版简介
Introduction to Rulers and Their Role in History

Throughout history, rulers have played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human civilization. From ancient empires to modern nations, the actions and decisions of rulers have had profound impacts on the societies they governed. This article explores the concept of rulership, the various types of rulers, and their significance in historical context.
Understanding Rulership

Rulership refers to the authority and power held by an individual or a group of individuals to govern a territory or a people. Rulers can be hereditary, elected, or appointed, and their roles can range from absolute monarchs to constitutional heads of state. The nature of rulership has evolved over time, reflecting changes in political, social, and economic structures.
Types of Rulers

1. Absolute Monarchs: These rulers hold absolute power and authority over their territories, with no legal constraints on their decisions. Examples include ancient Egyptian Pharaohs, Roman Emperors, and the Tsars of Russia.
2. Constitutional Monarchs: These rulers, while still part of the monarchy, have limited powers and are often ceremonial in nature. Their roles are defined by a constitution, which outlines the separation of powers between the ruler and other branches of government. Examples include the British monarch and the Japanese Emperor.
3. Dictators: Dictators are rulers who come to power through force or manipulation of the political system. They often hold absolute power and suppress political opposition. Notable dictators include Adolf Hitler, Joseph Stalin, and Kim Jong-un.
4. Democratic Leaders: These rulers are elected by the people and are accountable to them. They lead democratic governments and are subject to the rule of law. Examples include U.S. presidents, Indian prime ministers, and German chancellors.
The Significance of Rulers in History

Rulers have been instrumental in shaping the course of history in several ways:
1. Political Stability: Rulers provide a sense of stability and continuity in governance, which is crucial for the development of societies. They establish and maintain political institutions, laws, and order.
2. Economic Development: Rulers have played a significant role in promoting economic growth and development. They invest in infrastructure, encourage trade, and implement policies that benefit their people.
3. Cultural and Social Progress: Rulers have been responsible for fostering cultural and social progress. They sponsor the arts, education, and scientific research, leading to advancements in various fields.
4. Conflict and War: Unfortunately, rulers have also been the architects of conflict and war. Their decisions and policies have led to the loss of lives, destruction of property, and the suffering of countless individuals.
Challenges Faced by Rulers

Rulers face numerous challenges in their roles, including:
1. Maintaining Power: Rulers must constantly navigate the complexities of power dynamics to ensure their hold on authority.
2. Balancing Interests: They must balance the interests of various groups within their territories, including the elite, the middle class, and the poor.
3. Dealing with External Threats: Rulers must protect their territories from external threats, such as invasions, alliances, and trade disputes.
4. Adapting to Change: As societies evolve, rulers must adapt their policies and governance structures to meet the changing needs of their people.
Conclusion

Rulers have been central figures in the history of human civilization. Their roles, challenges, and impacts have varied widely, but their influence on the course of history cannot be denied. Understanding the nature of rulership and the diverse experiences of rulers can provide valuable insights into the complexities of governance and the factors that shape societies.
history rulership absolute_monarchy constitutional_monarchy dictator democratic_leader political_stability economic_development cultural_progress challenges_of_rulers governance